Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.

Bài 1:
a) Vì giá trị của biểu thức \(\frac{3x-2}{4}\) không nhỏ hơn giá trị của biểu thức \(\frac{3x+3}{6}\) nên \(\frac{3x-2}{4}\) \(\ge\) \(\frac{3x+3}{6}\)
TH1: \(\frac{3x-2}{4}\) = \(\frac{3x+3}{6}\)
=> (3x-2)6 = (3x+3)4
18x -12= 12x+12
=> x = 4
TH2: \(\frac{3x-2}{4}\) > \(\frac{3x+3}{6}\)
=> (3x-2)6 > (3x+3)4
18x-12> 12x+12
=> x \(\ge\) 5
b) Vì ( x+1)2 \(\ge\) 0; (x-1)2 \(\ge\) 0 mà (x+1) luôn lớn hơn (x-1) với mọi x nên không có giá trị của x thỏa mãn (x+1)2 nhỏ hơn (x-1)2
c) Phần c bạn cũng xét tương tự như phần a
TH1: \(\frac{2x-3}{35}+\frac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}=\frac{x^2}{7}-\frac{2x-3}{5}\)
TH2: \(\frac{2x-3}{35}+\frac{x\left(x-2\right)}{7}<\frac{x^2}{7}-\frac{2x-3}{5}\)

1.
|x-9|=2x+5
x<9; x-9=-2x-5
3x=4=>x=4/3(n)
x≥9; x-9=2x+5=> x=-14(l)
2.a
A=2x-5≥0<=>2x≥5; x≥5/2
1. a) / x - 9 / = 2x + 5
Do : / x - 9 / ≥ 0 ∀x
⇒2x + 5 ≥ 0
⇔ x ≥ \(\dfrac{-5}{2}\)
Bình phương cả hai vế của phương trình , ta được :
( x - 9)2 = ( 2x + 5)2
⇔ ( x - 9)2 - ( 2x + 5)2 = 0
⇔ ( x - 9 - 2x - 5)( x - 9 + 2x + 5) = 0
⇔ ( - x - 14)( 3x - 4) = 0
⇔ x = - 14 ( KTM) hoặc : x = \(\dfrac{4}{3}\) ( TM)
KL....
b) Mạn phép làm luôn , ko chép lại đề :
\(\dfrac{5\left(x+3\right)}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}+\dfrac{4\left(x-3\right)}{\left(x+3\right)\left(x-3\right)}=\dfrac{x-5}{\left(x-3\right)\left(x+3\right)}\) ( x # 3 ; x # - 3)
⇔ 5x + 15 + 4x - 12 = x - 5
⇔ 9x + 3 = x - 5
⇔ 8x = - 8
⇔ x = -1 ( TM)
KL....

b) \(\dfrac{5\left(4x-1\right)}{15}-\dfrac{2-x}{15}-\dfrac{3\left(10x-3\right)}{15}\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{20x-5-2+x-30x+9}{15}\le0\)
\(\Rightarrow-9x+2\le0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-9x\le-2\)
\(\Rightarrow-9x.\dfrac{-1}{9}\ge-2.\dfrac{-1}{9}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge\dfrac{2}{9}\)
câu a ,không hiểu đề

a)\(\dfrac{x-5}{4}\ge\dfrac{3-2x}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\dfrac{5x-25}{20}\ge\dfrac{12-8x}{20}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-25\ge12-8x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x+8x\ge12+25\)
\(\Leftrightarrow13x\ge37\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge\dfrac{37}{13}\)
b)\(2x\left(6x-1\right)-3< 3x\left(4x+3\right)-5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x^2-2x-3< 12x^2+9x-5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x^2-12x^2-2x-9x+5x< 3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x< 3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x>-\dfrac{1}{2}\)
c)\(\left|x-4\right|=5-3x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5-3x=x-4\\5-3x=4-x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}5+4=x+3x\\5-4=-x+3x\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}4x=9\\2x=1\end{matrix}\right.\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\left[{}\begin{matrix}x=\dfrac{9}{4}\\x=\dfrac{1}{2}\end{matrix}\right.\)
p/s: tui làm đúng đề
a.
\(\dfrac{x-5}{4}\ge\dfrac{3-2x}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5x-25\ge12-8x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow13x\ge37\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x\ge\dfrac{37}{13}\)
0 37 13
b.
\(2x\left(6x-1\right)-3< 3x\left(4x+3\right)-5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow12x^2-2x-3< 12x^2+9x-5x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-6x>3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< \dfrac{-1}{2}\)
0 -1 2

a, Vì \(2+\frac{3-2x}{5}\)không nhỏ hơn \(\frac{x+3}{4}-x\)
\(\Rightarrow2+\frac{3-2x}{5}\ge\frac{x+3}{4}-x\)
Giải phương trình :
\(2+\frac{3-2x}{5}\ge\frac{x+3}{4}-x\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{40}{20}+\frac{4\left(3-2x\right)}{20}\ge\frac{5\left(x-3\right)}{20}-\frac{20x}{20}\)
\(\Rightarrow40+12-8x\ge5x-15-20x\)
\(\Rightarrow7x=67\)
\(\Rightarrow x\ge\frac{67}{7}\)
b, \(\frac{2x+1}{6}-\frac{x-2}{9}>-3\)
\(\Rightarrow\frac{3\left(2x+1\right)}{18}-\frac{2\left(x-2\right)}{18}>\frac{-54}{18}\)
\(\Rightarrow6x+3-2x+4>-54\)
\(\Rightarrow4x>-61\)
\(\Rightarrow x>\frac{-61}{4}\)\(\left(1\right)\)
Và : \(x-\frac{x-3}{4}\ge3-\frac{x-3}{12}\)
\(\frac{12x}{12}-\frac{3\left(x-3\right)}{12}\ge\frac{36}{12}-\frac{x-3}{12}\)
\(\Rightarrow12x-3x+9\ge36-x+3\)
\(\Rightarrow10x\ge30\)
\(\Rightarrow x\ge3\)\(\left(2\right)\)
Từ \(\left(1\right)\)và \(\left(2\right)\)\(\Rightarrow\hept{\begin{cases}x>\frac{-61}{4}\\x\ge3\end{cases}\Rightarrow x>3}\)
Vậy với giá trị x > 3 thì x là nghiệm chung của cả 2 bất phương trình

a) \(x^2\) - x( x - 3) > 2x + 5
<=> \(x^2\) - \(x^2\) + 3x > 2x +5
<=> x > 5
Vậy bất phương trình có nghiệm x > 5.
Biểu diễn:
0 5
b) \(\dfrac{x\left(2x-1\right)}{12}\) - \(\dfrac{x}{8}\)< \(\dfrac{x^2-1}{6}\) - \(\dfrac{x+4}{24}\)
<=> \(\dfrac{4x^2-2x-3x}{24}\)<\(\dfrac{4x^2-4-x-4}{24}\)
<=> \(4x^2\) - 2x - 3x < \(4x^2\) - 4 - x -4
<=> -4x< -8
<=> x>2
Vậy bất phương trình có nghiệm x>2.
Biểu diễn:
0 2
![]()

a/ \(\dfrac{2-x}{3}< \dfrac{3-2x}{5}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow5\left(2-x\right)< 3\left(3-2x\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow10-5x< 9-6x\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x< -1\)
Bpt có tập nghiệm: \(S=\left\{x|x>-1\right\}\)
Biểu diễn tập nghiệm trên trục số:
-1 0
b/ 8x + 3(x+1) > 5x - (2x - 6)
<=> 8x + 3x + 3 > 5x - 2x + 6
<=> 8x + 3x - 5x + 2x > 6 - 3
<=> 8x > 3 <=> x > \(\dfrac{8}{3}\)
Vậy bpt có tập nghiệm là: \(S=\left\{x|x>\dfrac{8}{3}\right\}\)
Biểu diễn........(tự biểu diễn nhé quá dễ r)
c/ \(\left|x-7\right|=-2x+3\) (*)
+) Nếu \(x-7\ge0\Leftrightarrow x\ge7\) thì
|x - 7| = x - 7
(*) => x - 7 = -2x + 3
<=> x + 2x = 3 + 7
<=> 3x = 10 <=> x = \(\dfrac{10}{3}\)(loại)
+) Nếu x - 7 < 0 <=> x < 7
thì |x - 7| = 2x - 3
(*) => x - 7 = 2x - 3
<=> x - 2x = -3 + 7
<=> -x = 4 <=> x = -4 (nhận)
Vậy pt có 1 nghiệm x = -4
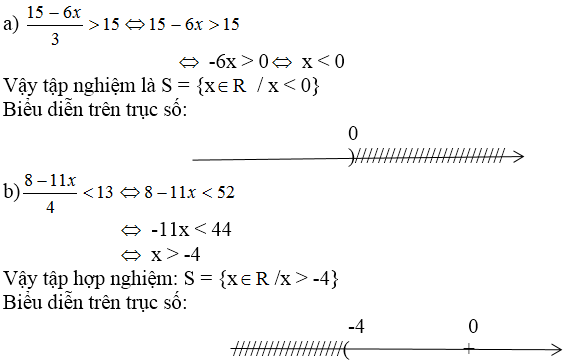
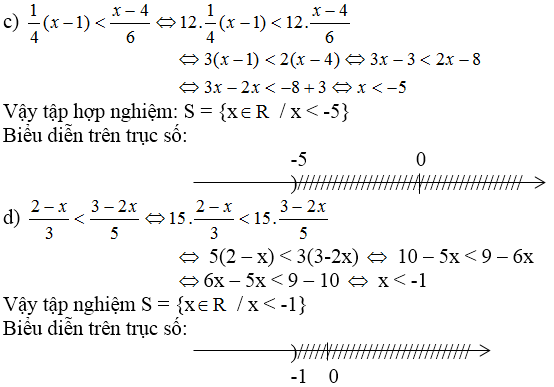
Câu 2:
a: 3x+4>2x+3
=>3x-2x>3-4
=>x>-1
b: =>8-11x<52
=>-11x<44
=>x>-4