
Hãy nhập câu hỏi của bạn vào đây, nếu là tài khoản VIP, bạn sẽ được ưu tiên trả lời.


\(a.\) \(\left(x^2+1\right)^2+3x\left(x^2+1\right)+2x^2=0\) \(\left(1\right)\)
Đặt \(t=x^2+1\) , khi đó phương trình \(\left(1\right)\) trở thành:
\(t^2+3xt+2x^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left(t+x\right)\left(t+2x\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(^{t+x=0}_{t+2x=0}\)
\(\text{*}\) \(t+x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x^2+x+1=0\)
Vì \(x^2+x+1=\left(x+\frac{1}{2}\right)^2+\frac{3}{4}\ne0\) với mọi \(x\) nên phương trình vô nghiệm
\(\text{*}\) \(t+2x=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x^2+2x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left(x+1\right)^2=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x+1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x=-1\)
Vậy, tập nghiệm của pt là \(S=\left\{-1\right\}\)
\(b.\) \(\left(x^2-9\right)^2=12x+1\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x^4-18x^2+81-12x-1=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x^4-18x^2-12x+80=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x^4-2x^3+2x^3-4x^2-14x^2+28x-40x+80=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(x^3\left(x-2\right)+2x^2\left(x-2\right)-14x\left(x-2\right)-40\left(x-2\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left(x-2\right)\left(x^3+2x^2-14x-40\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(\left(x-2\right)\left(x-4\right)\left(x^2+6x+10\right)=0\)
Vì \(x^2+6x+10=\left(x+3\right)^2+1\ne0\) với mọi \(x\)
\(\Rightarrow\) \(\left(x-2\right)\left(x-4\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\) \(^{x_1=2}_{x_2=4}\)
Vậy, phương trình đã cho có các nghiệm \(x_1=2;\) \(x_2=4\)

bài 1 :
\(\Rightarrow x=-\frac{1}{4}\) hoặc \(x=\frac{1}{2}\)
bài 2 :
\(\Leftrightarrow\left(2x+1\right)\left(3x+2\right)\left(12x+7\right)^2-3=\left(3x+1\right)\left(6x+5\right)\left(48x^2+56x+19\right)\)
\(\Rightarrow3x+1=0\)
\(\Rightarrow3x=-1\)
\(\Rightarrow6x+5=0\)
\(\Rightarrow6x=-5\)
Áp dụng Delta ta có :
\(\Rightarrow48x^2+56x+19=0\)
\(\Rightarrow56^2-4\left(48.19\right)=-512\)
=>D<0 ko có nghiệm thực ( ko có hình tam giác nên thay tạm )
\(\Rightarrow x=-\frac{5}{6}\) hoặc \(x=-\frac{1}{3}\)
tôi nhớ có 1 lần tôi làm mà ông ko tik nhé
a/ 2x(8x - 1)2(4x - 1) = 9
=> (64x2 - 16x + 1) (8x2 - 2x) = 9
- Nhân 2 vế cho 8 ta đc:
(64x2 - 16x + 1) (64x2 - 16x) = 72
- Đặt a = 64x2 - 16x ta đc:
(a + 1).a = 72
=> a2 + a - 72 = 0
=> (a - 8)(a + 9) = 0
=> a = 8 hoặc a = -9
- Với a = 8 => 64x2 - 16x = 8 => 64x2 - 16x - 8 = 0 => (2x - 1)(4x + 1) = 0 => x = 1/2 hoặc x = -1/4
- Với a = -9 => 64x2 - 16x = -9 => 64x2 - 16x + 9 = 0 , mà 64x2 - 16x + 9 > 0 => pt vô nghiệm
Vậy x = 1/2 , x = -1/4

\(D=\frac{x^2-3x+3}{x^2-2x+1}=\frac{x^2-3\left(x-1\right)}{\left(x-1\right)^2}\)
Đặt: x-1=y=>x=y+1. Ta có:
\(D=\frac{\left(y+1\right)^2-3y}{y^2}=\frac{y^2-y+1}{y^2}=1-\frac{1}{y}+\frac{1}{y^2}\)
Đặt: \(\frac{1}{y}=t\Rightarrow D=1-t+t^2\ge\frac{3}{4}\\ D=\frac{3}{4}\Leftrightarrow\left(t-\frac{1}{2}\right)^2=0\Rightarrow t=\frac{1}{2}\)
\(t=\frac{1}{2}\Leftrightarrow\frac{1}{y}=\frac{1}{2}\Rightarrow y=2\Leftrightarrow x-1=2\Rightarrow x=3\)
Vậy minD=\(\frac{3}{4}\Leftrightarrow x=3\)
D=\(\frac{x.x-3x+3}{x.x-2x+1}\)
D=\(\frac{x.\left(x-3\right)+3}{x.\left(x-2\right)+1}\)
D=\(\frac{x-3+3}{x-2+2}\)(Chia cả tử và mẫu cho x lần)
D=\(\frac{x}{x}\)
D=1

A)3x-2=2x+5
<=>3x-2x=5+2(chuyển vế hạng tử)
<=>x=7
b)4x+2=-3x-5
<=>4x+3x=-5-2(chuyển vế)
<=>7x=-7
<=>x=-1
Nếu đúng nhớ ấn đúng để cộng điểm cho mình nha

\(\left(2n-1\right)^3-\left(2n-1\right)\)
\(=\left(2n-1\right).\left[\left(2n-1\right)^2-1^2\right]\)
\(=\left(2n-1\right).\left(2n-1-1\right).\left(2n-1+1\right)\)
\(=\left(2n-2\right).\left(2n-1\right).2n\)
\(=2.\left(n-1\right).\left(2n-1\right).2n\)
Với \(n\)lẻ
\(\Rightarrow n-1\)chẵn
\(\Rightarrow n-1⋮2\)
\(\Rightarrow2.\left(n-1\right)⋮4\)
\(\Rightarrow2.\left(n-1\right).2n⋮8\)
\(\Rightarrow2.\left(n-1\right).\left(2n-1\right).2n⋮8\)(1)
Với n chẵn
\(\Rightarrow n⋮2\)
\(\Rightarrow2n⋮4\)
\(\Rightarrow2.\left(n-1\right).2n⋮8\)
\(\Rightarrow2.\left(n-1\right).\left(2n-1\right).2n⋮8\)(1)
Từ (1) và (2)
\(\Rightarrow\left(2n-1\right)^3-\left(2n-1\right)⋮8\forall x\inℤ\)
đpcm

a) Ta có: \(\frac{x+a}{x+2}+\frac{x-2}{x-a}=2\left(1\right)\)
Với a = 4
Thay vào phương trình (t) ta được:
\(\frac{x+2}{x+2}+\frac{x-2}{x-2}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}+\frac{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x+2\right)\left(x-2\right)}=\frac{2\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}{\left(x-2\right)\left(x+2\right)}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow x^2-4+x^2-4=2\left(x^2-4\right)\)
\(\Leftrightarrow2x^2=2x^2-8\)
\(\Leftrightarrow0x=-8\)
Vậy phương trình vô nghiệm
b) Nếu x = -1
\(\Rightarrow\frac{-1+a}{-1+2}+\frac{-1-2}{-1-a}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{-1+a}{1}+\frac{-3}{-1-a}=2\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\frac{\left(-1+a\right)\left(-1-a\right)}{-1-a}+\frac{-3}{-1-a}=\frac{2\left(-1-a\right)}{-1-a}\)
\(\Leftrightarrow1+a-a-a^2-3=-2-2a\)
\(\Leftrightarrow-a^2+2a=-2-1+3\)
\(\Leftrightarrow a\left(2-a\right)=0\)
\(\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}a=0\\2-a=0\end{cases}\Leftrightarrow\orbr{\begin{cases}a=0\\a=2\end{cases}}}\)
Vậy a = {0;2}
NĂM MỚI VUI VẺ

4(x-1)2=x2
<=>2(x-1)=x hoặc 2(x-1)=-x
<=>2x-2=x hoặc 2x-2=-x
<=>x=2 hoặc x=2/3
Vậy trung bình cộng các giá trị x là: (2+2/3):2=4/3
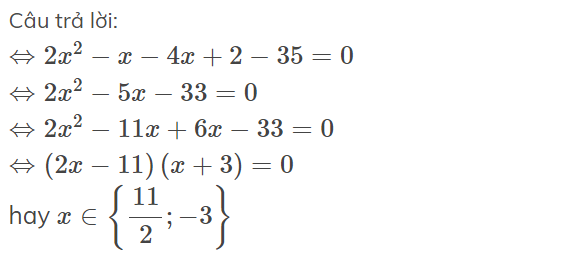
2C = 4x+2/x^2+2
2C + 1 = 4x+2+x^2+2/x^2+2
= x^2+4x+4/x^2+2
= (x+2)^2/x^2+2 > = 0
<=> 2C >= -1
<=> C >= -1/2
Dấu "=" xảy ra <=> x+2=0 <=> x=-2
Vậy Min của C = -1/2 <=> x=-2
2C = 4x+2/x^2+2
2C + 1 = 4x+2+x^2+2/x^2+2
= x^2+4x+4/x^2+2
= (x+2)^2/x^2+2 > = 0
<=> 2C >= -1
<=> C >= -1/2
Dấu "=" xảy ra <=> x+2=0 <=> x=-2
Vậy Min của C = -1/2 <=> x=-2
Tk mk nha